How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, opening doors to stunning aerial photography, videography, and even professional applications. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from understanding drone regulations and choosing the right equipment to mastering flight controls and capturing breathtaking visuals. We’ll explore essential safety procedures, advanced techniques, and troubleshooting tips, ensuring you’re well-equipped to take to the skies confidently and responsibly.
From the initial setup and calibration to navigating complex flight maneuvers and understanding battery management, we’ll demystify the process. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to enhance existing skills, this comprehensive guide will provide the knowledge and confidence to unlock the full potential of your drone.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to both legal requirements and crucial safety procedures. Failure to do so can result in accidents, fines, or even legal action. This section covers essential aspects of safe and legal drone operation.
Drone Laws and Regulations
Drone regulations vary significantly across countries and regions. Before flying, thoroughly research the specific rules in your area. Many jurisdictions require drone registration, licensing, and adherence to airspace restrictions near airports and other sensitive locations. For example, in the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) mandates registration for most drones and imposes restrictions on flight altitude and proximity to people and buildings.
Similarly, the UK’s Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) has its own set of regulations, including drone operator competency requirements. Always check the relevant aviation authority’s website for the most up-to-date information.
Pre-Flight Safety Procedures
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe operation. This checklist should be followed meticulously before every flight.
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage to propellers, arms, or body.
- Ensure the battery is fully charged and properly connected.
- Verify GPS signal strength and satellite lock.
- Check the controller’s battery level and connection to the drone.
- Review the weather conditions and avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or fog.
- Confirm the flight area is clear of obstacles and people.
- Check local airspace restrictions and obtain necessary permissions.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
A systematic pre-flight inspection is paramount. This checklist aids in identifying potential issues before takeoff.
| Item | Check |
|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for cracks or damage |
| Battery | Check charge level and secure connection |
| GPS Signal | Ensure strong signal and satellite lock |
| Camera | Verify functionality and settings |
| Controller | Check battery and connection |
| Airspace | Confirm no restrictions in flight area |
Common Drone Accidents and Causes
Understanding common drone accidents and their causes can help prevent them.
| Accident Type | Cause |
|---|---|
| Crash due to loss of signal | Interference, low battery, distance from controller |
| Collision with obstacle | Poor visibility, lack of situational awareness |
| Battery failure | Overuse, improper charging, age |
| Mechanical failure | Poor maintenance, component malfunction |
Choosing and Setting Up Your Drone
Selecting the right drone and properly setting it up are crucial for a positive flying experience. This section guides you through the process.
Drone Types and Features

Drones come in various types, each suited for different purposes and skill levels. Factors to consider include camera quality, flight time, range, features (like obstacle avoidance), and price. Beginner drones typically offer simpler controls and greater stability, while advanced models cater to experienced users seeking more features and maneuverability. Consider your budget and intended use (photography, videography, racing, etc.) when making your choice.
Setting Up Your Drone
Setting up a new drone involves several steps.
- Charge the drone battery fully according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Download and install the drone’s companion app on your smartphone or tablet.
- Connect the drone to the app following the app’s instructions. This usually involves enabling Bluetooth or Wi-Fi on your device.
- Calibrate the drone’s compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) sensors as per the app’s guidance. This ensures accurate flight data.
- Perform a pre-flight check before your first flight.
Selecting Propellers and Accessories
Choosing the right propellers and accessories enhances performance and safety. Propellers should match the drone’s specifications, and higher quality propellers generally offer improved stability and durability. Consider additional batteries for extended flight times and a carrying case for protection and transport.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Accurate calibration is vital for stable and precise flight. The process typically involves spinning the drone horizontally and vertically several times while following the instructions within the drone’s app. This calibrates the compass and IMU, ensuring accurate readings for flight control.
Mastering Drone Controls
Understanding and mastering drone controls is essential for safe and effective operation. This section details basic and advanced flight techniques.
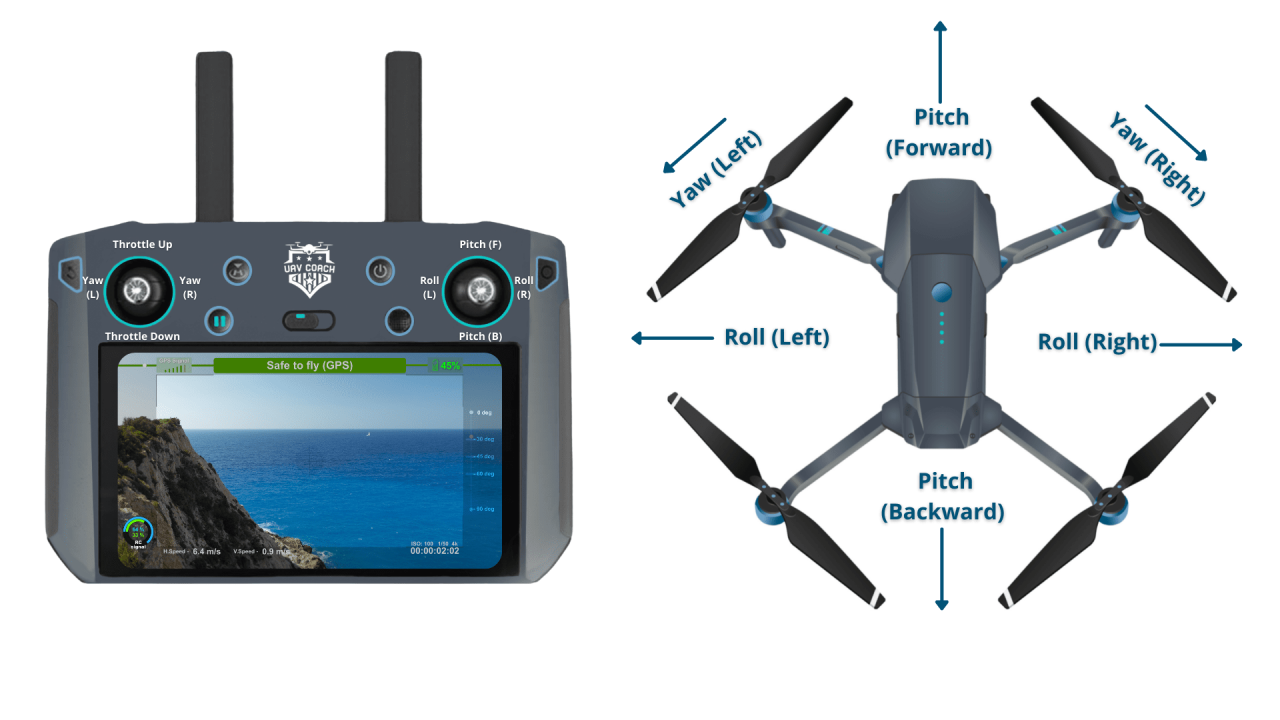
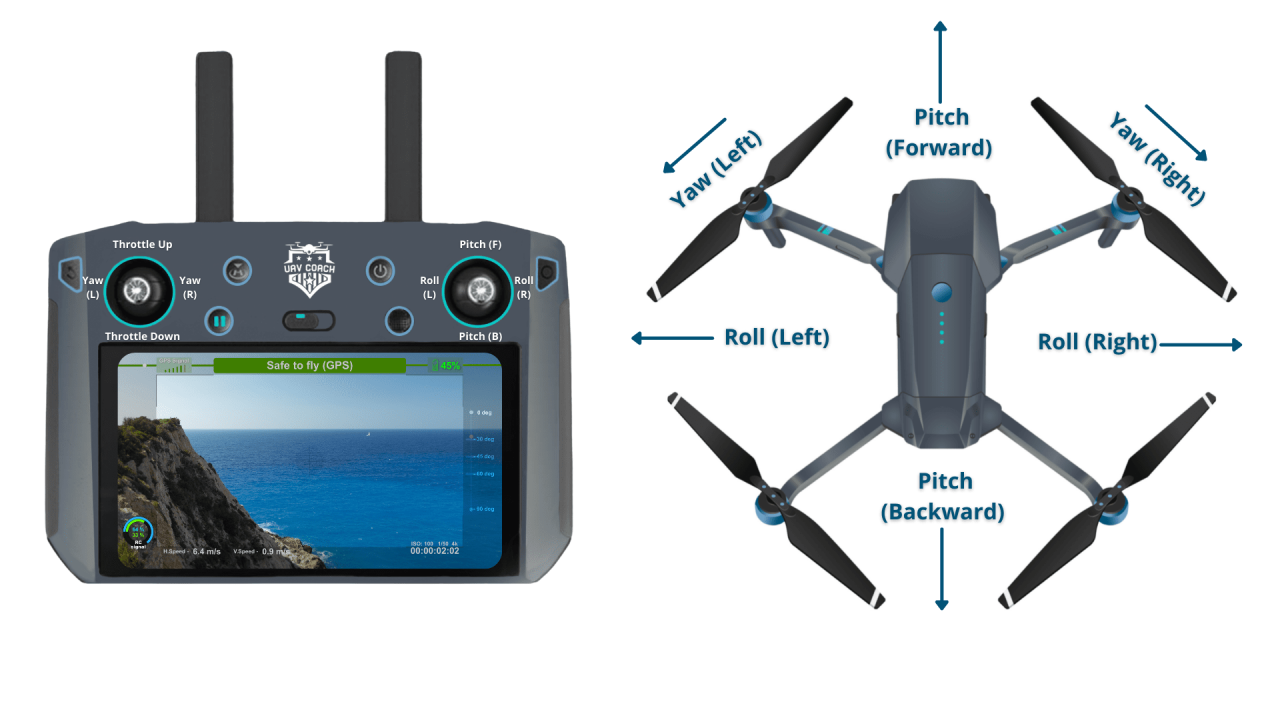
Basic Flight Controls
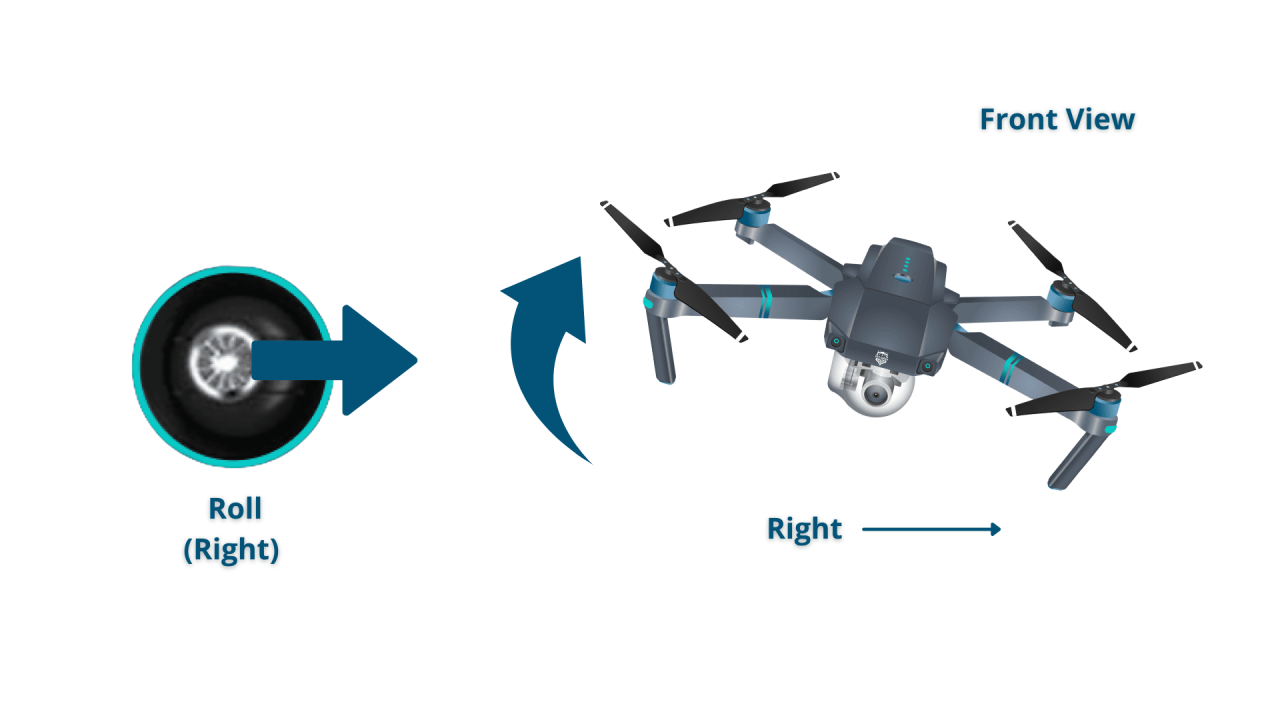
Most drones utilize four basic controls: throttle (controls altitude), yaw (rotates the drone left or right), pitch (tilts the drone forward or backward), and roll (tilts the drone left or right). These controls work in conjunction to allow for precise maneuvering.
Advanced Flight Modes
Many drones offer advanced flight modes to simplify piloting and enhance safety. Altitude hold maintains a constant altitude, simplifying vertical control. GPS mode allows for more precise positioning and automated flight features. Return-to-home (RTH) automatically guides the drone back to its starting point in case of signal loss or other emergencies.
Smooth and Precise Maneuvers
Smooth and precise maneuvers are achieved through gradual and controlled inputs to the flight sticks. Avoid jerky movements, which can destabilize the drone, especially in windy conditions. Practice in a safe, open area to build proficiency.
Common Flight Errors and Corrections
Common errors include drifting, uncontrolled yaw, and sudden drops in altitude. These can often be attributed to wind, battery issues, or improper calibration. Addressing these requires careful observation and corrective adjustments to the controls or a thorough pre-flight check.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which offers comprehensive tutorials and guides. This will help you confidently navigate the complexities of drone operation and ensure safe and responsible flying.
Taking High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
Capturing stunning aerial footage requires understanding factors affecting image quality and employing effective composition techniques. This section covers essential aspects of aerial photography and videography.
Factors Influencing Image Quality
Several factors influence image quality. Lighting conditions significantly impact exposure and detail. Adequate lighting prevents underexposed or overexposed images. Camera settings like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO influence sharpness, motion blur, and noise levels. Drone stability minimizes camera shake and improves image sharpness.
Using a higher resolution setting increases image detail.
Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Effective composition enhances visual appeal. The rule of thirds, leading lines, and framing are essential techniques. Experiment with different perspectives to create dynamic and engaging visuals. Consider the subject’s placement within the frame, leading lines to guide the viewer’s eye, and using negative space to enhance the subject’s prominence.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Adjusting camera settings like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is crucial for achieving desired results. A wider aperture (lower f-stop number) creates a shallower depth of field, blurring the background. Faster shutter speeds (higher shutter speed number) freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur. ISO controls image sensitivity to light, with higher ISO values introducing more noise.
Video Resolutions and File Sizes
Different video resolutions offer varying levels of detail and require different amounts of storage space. Higher resolutions produce sharper, more detailed videos but result in larger file sizes.
| Resolution | Approximate File Size (per minute) |
|---|---|
| 1080p | 100-200 MB |
| 4K | 300-600 MB |
| 2.7K | 200-400 MB |
| 1440p | 150-300 MB |
Drone Battery Management and Maintenance
Proper battery management and regular maintenance extend the lifespan of your drone and ensure safe operation. This section Artikels best practices.
Charging and Storing Batteries
Always charge batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions using the provided charger. Avoid overcharging, which can damage the battery. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
Signs of a Failing Battery, How to operate a drone
Signs of a failing battery include reduced flight time, rapid voltage drop during flight, and swollen or damaged casing. If you observe any of these signs, replace the battery immediately.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
Regular cleaning and inspection are essential. Clean the drone’s body and propellers after each flight to remove dirt and debris. Inspect for any damage or wear and tear. A routine maintenance schedule can significantly extend the lifespan of your drone.
Common Drone Maintenance Tasks
- Clean propellers and body after each flight.
- Inspect for any damage to the drone’s body, arms, and propellers.
- Check battery health and replace if necessary.
- Inspect and tighten all screws and connections.
- Calibrate the compass and sensors regularly.
- Store the drone and batteries in a cool, dry place.
Advanced Drone Techniques: How To Operate A Drone
This section explores advanced techniques for navigating challenging conditions and achieving cinematic shots.
Flying in Challenging Conditions
Flying in windy conditions requires careful control and anticipation. Adjust your flight speed and be prepared for unexpected gusts. Avoid flying in heavy rain or snow, as these can damage the drone’s electronics. Always prioritize safety over capturing the shot.
Waypoints and Automated Flight Planning
Many drones allow for waypoint programming, enabling automated flight along predefined paths. This feature is useful for complex shots or repetitive tasks. Proper planning and understanding of the drone’s capabilities are crucial for safe and successful automated flights.
Obstacle Avoidance and Strategies
Effective obstacle avoidance requires situational awareness and careful planning. Use the drone’s sensors (if equipped) to assist with navigation. Always maintain a safe distance from obstacles and be prepared to take immediate evasive action if necessary.
Achieving Cinematic Drone Shots
Cinematic shots involve using smooth, deliberate movements and creative compositions. Experiment with different camera angles, speeds, and movements to create visually stunning footage. Consider using slow, deliberate movements to create a sense of drama and tension.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires practice and knowledge of regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will help you confidently take to the skies and capture stunning aerial footage.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
This section provides solutions for common drone malfunctions.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Solutions
Common malfunctions include GPS issues, motor problems, low battery, and connectivity problems. GPS issues can often be resolved by moving to an area with a stronger signal. Motor problems may require professional repair or replacement. Low battery necessitates immediate landing. Connectivity problems can sometimes be solved by restarting the drone and controller or checking for interference.
Troubleshooting Connectivity Problems
Connectivity problems between the drone and controller can stem from interference, low battery, distance, or software glitches. Troubleshooting steps include checking the controller and drone batteries, moving closer to the drone, restarting both devices, and checking for software updates.
- Check the battery levels of both the drone and controller.
- Restart both the drone and the controller.
- Check for software updates for both the drone and the controller app.
- Ensure there is no significant interference from other electronic devices.
Troubleshooting Guide
Here’s a summary of troubleshooting steps for common issues.
If your drone is experiencing GPS issues, try moving to an open area with a clear view of the sky. Ensure sufficient satellites are acquired before attempting flight.
If a motor fails, land immediately and inspect the drone for damage. Do not attempt to fly with a malfunctioning motor.
If you experience connectivity problems, check for interference from other devices and restart both the drone and controller.
Drone Photography and Videography Composition
This section delves into composition techniques for creating compelling aerial visuals.
The Rule of Thirds
The rule of thirds suggests placing key elements along imaginary lines that divide the frame into thirds, both horizontally and vertically. This creates a more balanced and visually appealing composition.
Leading Lines and Framing
Leading lines draw the viewer’s eye through the image, creating a sense of depth and movement. Framing involves using elements within the scene to highlight the main subject, enhancing its visual impact.
Different Perspectives
Varying perspectives, such as high-angle shots, low-angle shots, and bird’s-eye views, create dynamic and engaging visuals. Experimenting with these perspectives adds visual interest and depth to your aerial footage.
Achieving a Dramatic Aerial Shot

A dramatic aerial shot can be achieved by utilizing low light conditions, creating a strong contrast between light and shadow. For example, imagine a lone building silhouetted against a vibrant sunset. The low light emphasizes the building’s form, while the sunset provides a captivating backdrop, enhancing the overall dramatic effect. A high angle shot, looking down on the building from a significant height, adds to the grandeur and scale of the scene.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding journey, blending technological understanding with creative vision. This guide has equipped you with the foundational knowledge and practical skills to navigate the skies safely and confidently. Remember, continuous practice, adherence to safety regulations, and a commitment to responsible flying are crucial for a positive and enriching drone experience. Soar above the ordinary and capture the world from a unique perspective!
User Queries
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones cater to beginners, often prioritizing ease of use and safety features. Research models with features like GPS stabilization and return-to-home functionality.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your drone’s compass before each flight is recommended, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced interference.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If signal is lost, the drone should automatically return to its takeoff point. Always keep the drone within visual line of sight.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, usage (flight time and features used), and battery condition. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
